•Storage holds data, instructions, and information for future use
•A storage medium / media is the physical material on which a computer keeps data, instructions,
and information
STORAGE CAPACITY
•Capacity is the number of bytes a storage medium
can hold
Capacity
Storage Measured in
•Kilobytes = 1,024 bytes,
•Megabytes = 1,024 Kilobytes
•Gigabytes = 1,024 Megabytes
•Terabytes = 1,024 Gigabytes
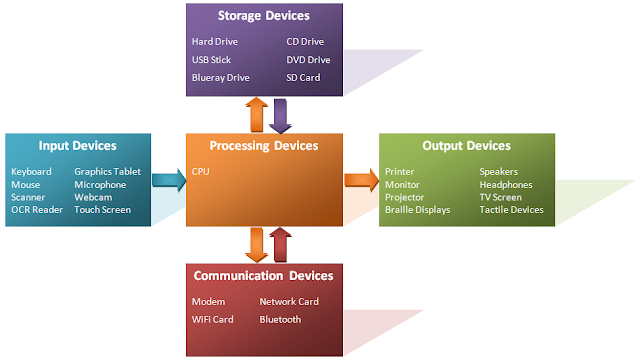
STORAGE DEVICES
•A storage
device is the computer hardware that
records and/or retrieves
items to and from storage
media
•To store data and
programs when they are not being
processed.
•Stores files
permanently.
•Available in the form
of hard disk, CD, USB drive,
etc.
TYPES OF STORAGE
•Magnetic Storage
•Optical Storage
•Flash memory
MAGNETIC STORAGE
–Uses
different patterns of magnetization on a magnetically coated surface to store
information.
–Examples of
magnetic
storage are:
Hard
Disk
Floppy disk
HARD DISK
•A hard
disk contains one or more inflexible, circular
platters that
use magnetic particles to store data,
instructions, and information
•An external hard disk is a separate free-standing hard disk that connects
to your computer with a
cable or wirelessly
•A removable hard disk is a hard disk that you insert and remove from a
drive
•Internal and external hard disks are available in miniature sizes
(miniature hard disks)
OPTICAL DISCS STORAGE
–Stores
information in deformities on the surface of a
circular disc and reads this
information by
illuminating the surface with a laser diode and
observing the
reflection.
–Types of
optical
disc are:
»Compact
Disc (CD)
»Digital
Video Disc (DVD)
»Blu-ray Disc (BD)
•A CD-ROM can be read from but not written to
-Read from a CD-ROM drive or CD-ROM player
•A CD-R is a multisession optical disc on which users can
write, but not erase
•A CD-RW is an erasable multisession disc
•A DVD-ROM is a high-capacity optical disc on which users can
read but not write or erase
-Requires a DVD-ROM drive
•A Blu-ray Disc-ROM (BD-ROM)
has a storage capacity of 100 GB
•DVD-RW, DVD+RW, and DVD+RAM are
high-capacity rewritable DVD formats
FLASH MEMORY STORAGE
•Flash memory chips are a type of solid state media and
contain no moving parts
–Examples of
flash
memory storage are:
1) solid states drives
2) memory card
3) USB flash drives
SOLID STAES DRIVES
•Solid state drives (SSDs) have several
advantages over magnetic hard disks:
-faster access time
-faster transfer rates
-generate less heat and consume less power
-last longer
STORAGE CAPACITY DIFFERENCES TABLE
(between magnetic, optical and flash memory)
COMPARE MEMORY AND STORAGE